Tax saving tips for small businesses in 2020

Tax & Auditing
273 week ago — 9 min read
Background: Minimising tax burden is a vital factor for the financial wellbeing of businesses. Vertika Kedia, founder-CEO of Tax2Win shares in detail important tax saving tips for SMEs.
Just like ‘a pitcher fills drop by drop’ the same holds true for every little tax saving for SMEs. Starting a business comes with a lot of statutory compliances that can become a burden in due course. In this article, I will try to reduce your tax burden by acquainting you with tax saving tips for small and medium businesses for the financial year 2020.
Plan smartly and save taxes!
Avoid expenditures in Cash [Section 40A(3)]
We are moving towards a digital economy but still cash payments are an integral part of our economy. People still find it the most convenient mode of payment. But the same is strictly not recommended for business expenditures, here is why:
- Any business cash payment which exceeds INR 10,000 is entirely disallowed
- If payment is made to a transporter then limit is INR 35,000
- Any payment by bearer cheque shall also be considered equal to cash payment
Let us understand it better with the help of an example:
M/s ABC made a cash payment of INR 50,000 in relation to business expenditure. What shall be the tax treatment?
In this situation the entire INR 50,000 shall be disallowed as an expenditure. As a result, M/s ABC will end up paying additional tax of INR 15,600.
Unreasonable payments to relatives [Section 40A(2)]
In the course of business, dealing with relatives is normal. You should always be cautious while making a business deal with your relative(s). If any payment related to business expenditure is made to a relative, then any excess unreasonable amount may be disallowed by the assessing officer.
You may think, 'On what basis will the assessing officer decide that the payment is unreasonable?'
The assessing officer will compare the market price of the same transaction and any excess payment may be disallowed.
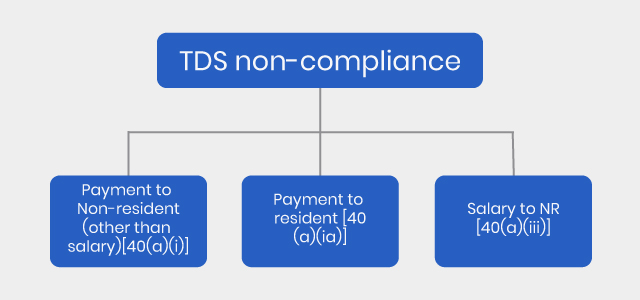
Avoid TDS non-compliance
TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) non-compliance does not only result in fine and penalties, but TDS non-compliance also results in disallowance of expenditure to a certain extent.
Also read: 7 tips for the new financial year
Payment to non-resident (other than salary)
If any payment is made to NRI on which TDS is required to be deducted but:
- TDS is not deducted or
- TDS is deducted but not deposited to the government
then 100% of such amount shall be disallowed.
Payment to resident
If any payment is made to a resident like commission, interest, professional fees on which TDS is required to be deducted as per the provisions of the Income Tax Act but
- TDS is not deducted on such payment or
- TDS is deducted but not deposited to the government
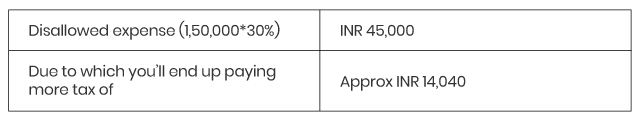
then 30% of the sum will be disallowed.
For example, ABC has made a payment of professional fees of INR 1,50,000 on which TDS is required to be deducted but the same has not been done. In this case, the amount disallowed will be
Salary payment outside India or to non-resident
If any payment of salary is made outside India or to NRI and if
- TDS is not deducted on such payment or
- TDS is deducted but not deposited to the government
then 100% of such sum shall not be allowed as a deduction.
TDS payment in subsequent years
If TDS is deducted in subsequent year or deducted in previous year but paid to government after the due date of return filing, then such disallowed sum will be allowed in the subsequent year. However, in the case of salary payment outside India or to non-resident, then expenses will not be allowed even if TDS deducted or paid in subsequent years.
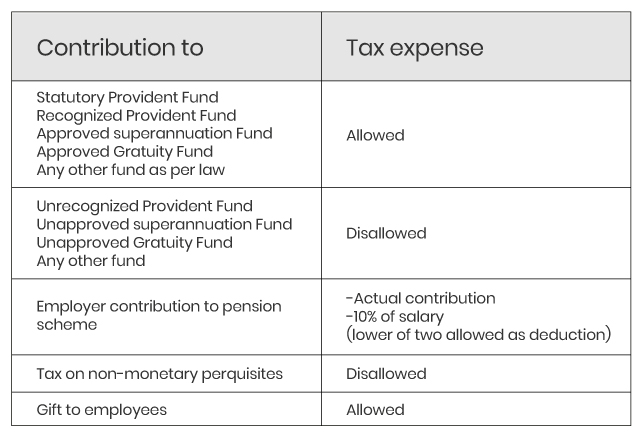
Employee related expenses
Employees are the most important asset of any organisation and many business expenses are incurred in relation to them. This includes:
- Health Insurance premium for employees
Deduction of health insurance premium is allowed only if payment is made in any mode other than cash.
- Bonus or commission to employees
Deduction of bonus or commission can be claimed in case payment is actually made before return filing.
- Employer’s contribution for the benefit of employee
Also read: A list of tax benefits for startups in India
Bad debts and provision for bad debts
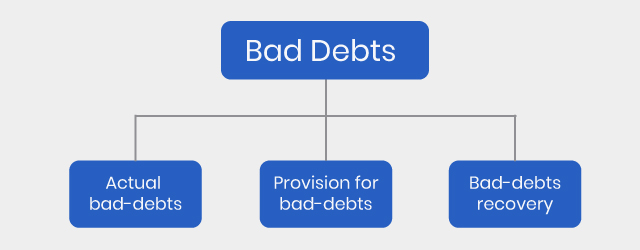
Bad debts
Deduction of bad debts can be allowed subject to the following conditions:
- Bad debts written off in the books of accounts.
- Debtors should have been taken into account for computing income in previous years.
- There is no need to prove that debts have become bad.
Provision for bad debts
Provision for bad debts is not allowed as deduction except in the case of banks (subject to certain conditions).
Recovery of bad debts
If any bad debts is allowed as deduction in previous years but now same has been recovered. Such recovery of bad debts shall be taxable in the year of recovery.
Taxes, Interest and Penalties
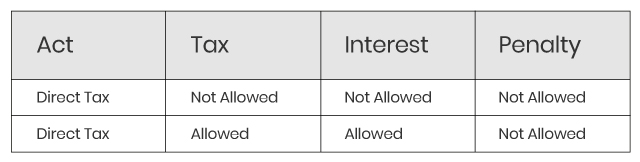
You must avoid late filing of tax returns whether related to direct tax or indirect tax since it results in heavy amount of penalties and deduction of penalties also not allowed.
General Deduction
Any expenditure shall be allowed as a deduction subject to following conditions:
- Expenses should be incurred exclusively for business purpose.
- Expenses should be revenue in nature.
- Expense should be legal.
List of some common expenses
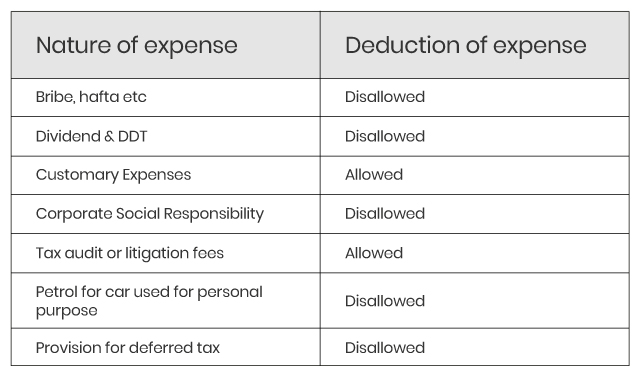
File your Income Tax Return
You should always file your Income tax return on time due to following reason
- To avoid late payment fees
- Interest on delay filing of return u/s 234A
- Delay in refund
- To carry forward your losses arising from business activity which you can set off from future profits.
Also read: Benefits of filing Income Tax Returns (ITR)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Is there any option for small businesses to pay taxes under presumptive scheme?
A. Business having turnover up to INR 2 crore may opt presumptive scheme u/s 44AD and can show 6%/8% of gross turnover as income.
Q. What is the due date of filing income tax return for individual having income from business & profession?
A. The due date of filing return is 31st July 2020. However, if tax audit is applicable then date is 30th September 2020. The due dates are subject to extension by CBDT (Central Board of Direct Taxes).
Q. Are there any exceptions to disallowance of cash expenses under section 40A(3)?
A. There are some exceptions of section 40A(3) which is given under Rule 6DD. In the following scenarios even if business expense is made in cash that too for an amount exceeding INR 10,000 the same would be allowed as an income tax expense.
1. Where the payment is made to:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) or any other bank
- Co-operative bank or Land mortgage bank
- State Bank of India (SBI) and its subsidiaries
- Primary agricultural society or Primary credit society
- Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC)
2. When a payment is made through
- Letter of credit (LC) issued by a bank
- Bills of exchange payable to bank only
- Mail or telegraphic transfer originated through a bank
- Payment made using credit/debit card
- Electronic clearing system made through the bank account
3. The adjustment made in books of account in case where payment is the adjustment which is being made for offsetting liability incurred by the assessee to the payee for the goods or services.
4. When payments are made to an individual
- For procuring produces of cottage industries operating without the aid of electrical power.
- Who is living in a village or town which doesn’t have facilities of a bank or carrying on business.
- For salary and employee must be temporarily posted for a period of 15 days or more, outside the normal place of duty. Also, s/he does not have any active bank account which is serviceable at such place of posting.
- On a banking holiday.
- To his agent who in turn makes payment for the procurement of goods or services on behalf of such assessee.
- For purchasing traveller’s cheques or foreign currency and payments made only to the authorized money changers.
- Or to government compulsorily required to be made in cash only.
Image source: shutterstock.com
To explore business opportunities, link with me by clicking on the 'Connect' button on my eBiz Card.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views, official policy or position of GlobalLinker.
View Vertika 's profile
Other articles written by Vertika Kedia
270 week ago
Most read this week
Trending
Ecommerce 1 week ago










Comments
Share this content
Please login or Register to join the discussion